Nutrition for Improved Liver Function. What Is the Liver?
- Nutrition for Improved Liver Function. What Is the Liver?
- Non alcoholic fatty liver Disease. Взаимодействия между метаболизмом триптофана, кишечным микробиомом и иммунной системой, как потенциальные факторы неалкогольной болезни печени (
- How to protect the liver. Ways to protect your liver
- Liver cleanse. Комплекс для очищения печени, Liver Cleanse, Thorne Research, 60 капсул
- Diet for liver Disease. Liver Disease & Diet for Health
- Cirrhosis Diet. Adequate foods for cirrhosis
- Liver Enzymes
- Best foods for liver. The 9 best and worst foods for your liver
- Liver Health. Liver Awareness Month Feature
Nutrition for Improved Liver Function. What Is the Liver?
What is the liver, and why is it considered one of the hardest working organs in the body?
The liver, the largest internal organ in the human body, is a digestive organ that sits on the upper right side of the belly. What does the liver look like? It’s described as being “meaty” due to its reddish-brown color. If you were to touch your liver, it would feel rubbery and semi-firm.
The liver is always communicating with other digestive organs, receiving information about the level of available nutrients or the presence of threats like prescription medications, heavy metals or toxic substances. As the main organ involved in detoxification, it’s the liver that recognizes toxic substances and converts them into harmless material that can be released. As described in the World Journal of Hepatology in a 2017 article , “Beyond the metabolic functions, the liver recently has been defined as an organ of immune system (IS) … The liver keeps a delicate balance between hepatic screening of pathogenic antigens and immune tolerance to self-antigens.”
Ad
The liver is said to be of the “wood element” and is crucial for the transformation of food into energy, or qi, according to Chinese medicine. Since it’s associated with wood qi , the liver is characterized by “upward momentum and the innate desire to be straight.” A healthy liver results in better blood flow upward and outward, throughout our vessels, veins and capillaries , which transport oxygen and nutrients to our cells.
Non alcoholic fatty liver Disease. Взаимодействия между метаболизмом триптофана, кишечным микробиомом и иммунной системой, как потенциальные факторы неалкогольной болезни печени (
Charlotte Teunis, Max Nieuwdorp and Nordin Hanssen
Interactions between Tryptophan Metabolism, the Gut Microbiome and the Immune System as Potential Drivers of Non-Alcohol Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Metabolic Diseases
Резюме
Распространенность неалкогольной жировой болезни печени () растет и, следовательно, является ее бременем, поскольку НАЖБП является фактором риска цирроза и ассоциируется с другими метаболическими заболеваниями, такими как диабет II типа, ожирение, дислипидемия и атеросклероз. Связь между этими кардиометаболическими заболеваниями заключается в состоянии воспаления низкой степени тяжести с более высокими уровнями цитокинов и С-реактивного белка , обнаруживаемыми у лиц с НАЖБП, ожирением и диабетом II типа. Возможной терапевтической мишенью для уменьшения этого состояния слабого воспаления является метаболизм незаменимой аминокислоты триптофана. Его три основных метаболических пути (,и) приводят к образованию таких метаболитов, как кинуреновая кислота , ксантуреновая кислота , индол-3-пропионовая кислота (IPA) и серотонин / мелатонин . Кинурениновый путь регулируется индоламин 2,3-диоксигеназой ( IDO ), ферментом, который активируется провоспалительными молекулами, такими как INF ,и ЛПС . Более высокая активность IDO связана с усилением воспаления ипри НАЖБП, а также с повышением уровня глюкозы, ожирением и атеросклерозом. С другой стороны, повышенные концентрации метаболитов индольного пути, регулируемые кишечным микробиомом, по-видимому, приводят к более благоприятным исходам. В этом описательном обзоре обобщены взаимодействия между метаболизмом триптофана, микробиомом кишечника и иммунной системой как потенциальными факторами кардиометаболических заболеваний при НАЖБП.
How to protect the liver. Ways to protect your liver
The liver is the second largest organ in the human body after the skin , which is situated below the diaphragm in the abdominal-pelvic region of the abdomen. This organ has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, production of some bio-chemicals necessary for digestion, glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, and hormone production. It produces bile, an alkaline compound which aids in digestion via the emulsification of lipids .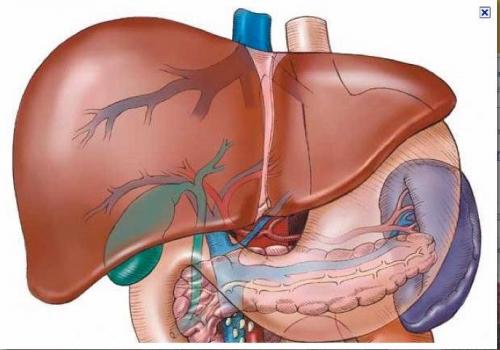
The liver is virtually responsible for processing every nutrient consumed – protein, fat or carbohydrate. This means that everything consumed passes through the liver, so this organ is subjected to an array of toxins – pesticides, hormones, food additives, alcohol, medications, microorganisms, and more-on a regular basis. The liver works as a filter for these harmful substances. To protect the body from their influence, it converts these toxins into less harmful ones or eliminates them entirely. However, sometimes, some toxins get left behind, hiding in certain liver cells or creating free radicals that can damage the liver and endanger the state of health. This is the reason why it is relly important to support your liver health in every way you can: through the food you eat, the medications you take, the drinks you consume.
How can you protect your liver?
1. Eat organic foods – Eating foods that are not contaminated with pesticides, growth hormones and chemical additives, is a good way to protect your liver’s health . Organic foods is the food free from genetically modified organisms, synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, antibiotics, growth hormones and other drugs.
2. Avoid fructose and trans fats – It was scientifically proven that a diet high in fructose and trans fats leads to obesity and fatty liver disease.
3. Eat fresh fruits and vegetables – Sulfur-rich foods, such as onions, garlic, broccoli, kale, collard greens, Brussels sprouts, cabbage, cauliflower are the best option for detoxifying your liver from environmental toxins, including prescription drugs and pesticides.
4. Avoid alcohol – The alcohol can destroy liver cells and lead to liver damage that causes fatty liver, inflammation, alcoholic hepatitis or cirrhosis.
5. Limit the use of chemical household products – The more chemicals you are exposed to, the harder your liver has to work to keep you healthy. Natural cleaning products and natural personal care products for your body are highly recommended.
6. Detoxify your body regularly – Detoxing can help to support and enhance the process of elimination of toxins from your body.
7. Use medication correctly – Taking medications in improper doses, for too long, or mixed with other substances, such as alcohol or other drugs, can harm your liver.
8. Avoid smoking – Smoking makes the process of elimination of the toxins from the body really hard.
9. Take liver supportive supplements – It can help support liver health .
Keep in mind that a strong liver is one of your best defenses against the toxins bombarding your body on a daily basis.
Liver cleanse. Комплекс для очищения печени, Liver Cleanse, Thorne Research, 60 капсул
Уникальная комбинация растительных ингредиентов, которые синергетически поддерживают функцию печени.
Liver Cleanse усиливает выработку и отток желчи, оптимизируя метаболизм и выведение веществ, которые печень детоксифицирует. Препарат направлен на общую поддержку печени или как часть программы детоксикации.
Артикул: SF769
Наличие: Есть в наличии
Этот товар в категориях
Описание
- Новая формула с цикорием.
- Произведено с натуральным ароматизатором.
- Не содержит глютен.
- Не содержит молочные продукты.
- Не содержит сою.
Для правильной детоксикации необходима нормальная работа печени. Ряд растительных веществ продемонстрировал свою способность улучшать функцию детоксикации печени, а также усиливать выработку желчи печенью.
Liver Cleanse от Thorne — это уникальная растительная формула, которая может синергетически усиливать функцию печени. Растительные ингредиенты в Liver Cleanse способствуют выработке и потоку желчи, что помогает оптимизировать метаболизм и выведение веществ, детоксицированных печенью. Liver Cleanse особенно полезен во время комплексной программы детоксикации.
Перед началом программы детоксикации важно добиться оптимальной работы кишечника. Поэтому важно включить в состав препарата клетчатку, такую как FiberMend® от Thorne, для поддержки выведения токсинов из организма путём связывания токсинов, выделяемых печенью в кишечник, и предотвращения их повторного всасывания.
Печень использует двухфазный метод детоксикации. В первой фазе жирорастворимые вещества, включая токсины, преобразуются ферментами цитохрома p450 в промежуточные вещества, которые, хотя и стали более водорастворимыми, ещё не готовы к выведению. Затем, на фазе II, промежуточные вещества, созданные на фазе I, присоединяются к глутатиону, сере или метиловым группам, что делает их достаточно водорастворимыми, чтобы они могли быть выведены из печени с желчью.
Рекомендации по применению
Принимайте по 1 капсуле 1-3 раза в день. Перед применением рекомендуется проконсультироваться с врачом и подобрать систему лечения. Не является лекарственным средством.
Дополнительные ингредиенты
Лаурат кальция, капсула из гипромеллозы, диоксид кремния.
| Дополнительные факты | ||
| Размер порции: одна капсула | ||
| Одна капсула содержит: | Количество на порцию | %DV |
| Берберин гидрохлорид (из экстракта индийского барбариса) (корень) (Berberis aristata) | 125 мг | * |
| Экстракт расторопши пятнистой (плоды) (Silybum marianum) | 125 мг | * |
| Экстракт лопуха (корень) (Arctium lappa) | 100 мг | * |
| Экстракт цикория (корень) (Cichorium intybus) | 100 мг | * |
| * Дневная норма (DV) не установлена. |
Diet for liver Disease. Liver Disease & Diet for Health
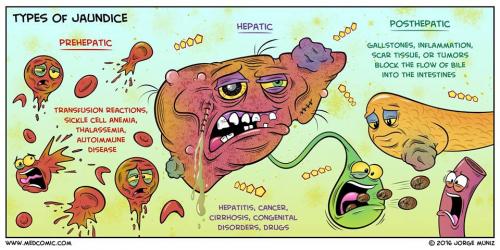
Liver Diseases :
- Jaundice
- Liver Cirrhosis
- Acute & Chronic Liver Failure
- Diet for Liver Health.
Please seek Medical attention as soon as possible if you are unsure of you or your family's health condition.
Liver Cirrhosis - Signs & Symptoms
Liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis , is a condition in which the liver does not function properly due to long-term damage. This damage is characterized by the replacement of normal liver tissue by scar tissue. Typically, the disease develops slowly over months or years.
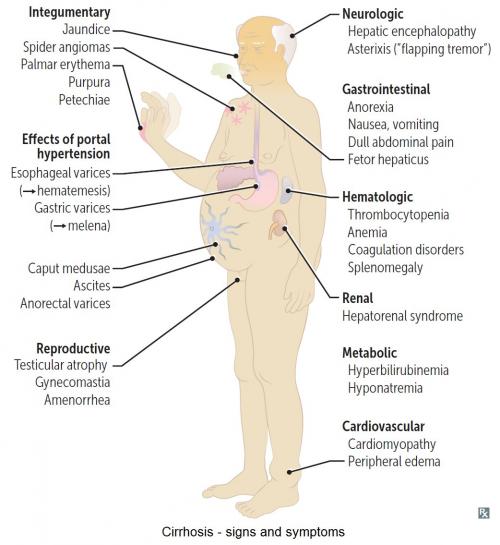
Acute Liver Failure
Acute liver failure is loss of liver function that occurs rapidly — in days or weeks — usually in a person who has no pre-existing liver disease . Acute liver failure is less common than chronic liver failure , which develops more slowly.
Chronic Liver Failure - Cirrhosis Symptoms
Chronic Liver Failure (CLF) is a disease process of the liver that involves progressive destruction and regeneration of the liver parenchyma leading to fibrosis and cirrhosis. Venous flow into the liver decreases due to this, leading to elevated portal pressures.
It can take months or even years before you exhibit any symptoms, as scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue. This stops the liver from working normally.
Health Assessment & Screening Packages
Sinopharm COVID-19 & Latest Influenza Vaccines (Protects against Flu and H1N1 Viruses) / PCR COVID Testing / Serology Tests for Travellers &Serology Testing to Certify Vaccination status. Make your Appointment at Tel: 6694 1661 |
Healthy Diets for Optimal Health
2020 Apr 23;12(4). pii: E1181. doi: 10.3390/nu12041181 Optimal Nutritional Status for a Well-Functioning Immune System Is an Important Factor to Protect against Viral Infections 1 , 2 , 3 ,
Up to $400 per Medisave Account per year can be used for Vaccinations under the National Adult & Childhood Immunisation Schedule - Influenza, Pneumococcal (PCV13/PPSV), Human Papillomavirus (HPV2/HPV4), Hepatitis B, Tetanus, Diphtheria & Pertussis (Tdap), Measles, Mumps & Rubella (MMR) and Chickenpox (Varicella) |
Part of the National Influenza Sentinel Surveillance programme with MOH. If you have a fever of > 38 degrees with a cough, our clinic is able to test for COVID-19. For children below 12 years old with clinical diagnosis of HFMD (eg fever, oral ulcers, rash), our clinic can test for Hand Foot & Mouth Disease (The tests are for surveillance purposes only).
- Flu Vaccine
- Childhood & Adult Vaccine schedule (Refer to NAIS & NCIS)
National Adult & Childhood Immunisation Schedule - Influenza, Pneumococcal (PCV13/PPSV), Human Papillomavirus (HPV2/HPV4), Hepatitis B, Tetanus, Diphtheria & Pertussis (Tdap), Measles, Mumps & Rubella (MMR) and Chickenpox (Varicella)
Co-infection of COVID-19 with other infectious diseases is possible
Reduce your risk of getting sick with COVID-19
- Make sure your vaccinations are up-to-date. People older than 65 years, and those with many underlying conditions, such as those who are immunocompromised or with significant liver disease, are recommended to receive vaccinations against Influenza and pneumococcal disease (PCV).
- Do not delay getting medical care for your underlying condition because of COVID-19. MD International Medical Centre has contingency MOH infection prevention protocols to protect you from getting COVID-19 if you need care for your underlying condition.
- Continue your medications and do not change your treatment plan without talking to your doctor.
- Make sure that you have at least a two-week supply of your chronic disease medications .
- Call MDIMC @ Tel: 6694 1661 for a medical appointment if you have any concerns about your underlying medical conditions or if you get sick. Our clinic is a PHPC-accredited medical clinic. Under the MOH Swab & Go Home programme, our doctors can do a COVID-19 PCR Swab test if you meet the MOH medical crtieria.
Cirrhosis Diet. Adequate foods for cirrhosis
ADEQUATE FOOD IN THE DIET OF CIRRHOSIS
| ©Dibujosparapintar.com |
In general, we can say that the most suitable foods for patient with cirrhosis are organic foods free of pesticides.
Compared to industrial food (full of preservatives, colorants and other chemical toxins), foods that have been produced organically (without pesticides, chemical fertilizers or other toxins) are best suited for a diseased liver.
This organ can not be obliged to assume an additional stress of removing these products, especially when it has to recover from an illness.
The most adequate important foods in the diet of cirrhosis are:
Fruits and vegetables for cirrhosis
Plant foods, especially fruits and vegetables, are best suited for liver patients. They are much easier to digest than meat so they do not impose a great effort to a diseased liver. Moreover,are rich in, minerals and.
Eating plenty of vegetables and fruits helps restore any possible nutrient deficiency that may cause cirrhosis.
On the other hand, antioxidants neutralize free radicals that can affect or worsen the liver health. We must not forget that fruits and vegetables contain lots of fiber which promotes more rapid evacuation of faeces and non-absorption of toxins through the intestine.
Fruits also possess more assimilable sugars than other foods containing refined sugars (refined flour derivatives, such as cakes, biscuits, candies, ice-creams, etc)
Fruits are more convenient than sugary foods because they are easier to digest and because they stabilize the levels of blood sugar better. When you feel the need to eat something sweet, it is better for you to take some fruit than a piece of candy.
Proteins for cirrhosis
Animalmay be responsible for the body to produce more ammonia than a person with cirrhosis may be unable to expel. Excess of ammonia in the body may damage the brain of this patient. Proteins from plant origin or even those fromdoes not produce such a quantity of ammonia and, therefore, they are more desirable in a diseased liver which has not to struggle so much to eliminate this toxin.
However, plant proteins are considered incomplete proteins. To assimilate vegetable proteins, we should be able to combine different types of plant foods so some deficiencies can be covered. For example, cereals are low inbut rich inand cystine. Legumes have lowand cystine but they are very rich in lysine. Combining, for example,with lentils we obtain a balanced combination of proteins. When we combine both foods, we get proteins similar in quality to those of meat.
A good way to get high quality proteins for ovo-lacto-vegetarian people is to combine eggs or milk (or dairy products) with plant foods.
Suitable fat for cirrhosis
In front of animal, the more interesting fats for cirrhotic patients are unsaturated fats which have been not subjected to any manipulation in the extraction process. Talking about oil, among all of them, one of the most interesting is the virginoil. Other interesting oils areor soybean oil.
Another great way to acquire right fats is to eat plant foods containing polyunsaturated fats rich in essential fatty acids, such as nuts, avocados or.
Especially recommended foods for the treatment of cirrhosis
Among the most interesting food for cirrhosis diet we have:
Artichokes are recommended for cirrhosis |
–: They contain cynarin, one of the most beneficial ingredients to protect the liver and help heal any condition that might affect it. Eating plenty of artichokes is a way of protecting the liver or preventing liver disease progression.
–: The fresh leaves of this wild herb protects the liver. A good way to increase its power is to combine artichoke leaves with dandelion leaves, adding,or other plants with very high antioxidant properties that can contribute to remove toxins.
–: It’s an edible wild plant whose young leaves can be added to salads and have a restorative function of liver cells. It helps the body eliminate toxins, making it especially interesting when the diseased liver needs this help.
–: Thecontent in chickpeas is higher than in other legumes such as soybeans or peanuts. Lecithin is necessary for the formation of choline. choline helps the liver to prevent or treat a variety of diseases that can affect it, such as cirrhosis, hepatitis, liver cancer or degradation of the liver caused by toxins.
Juice therapy for cirrhosis
Using juice from fruits or vegetables is highly recommended for those suffering from cirrhosis. This type of juice has many antioxidants that are able to help the liver neutralize toxins.
More information cirrhosis and its natural treatment
This article was endorsed by- Dietitian nutritionist. Postgraduate in Phytotherapy and master in Nutrition and Metabolism.
Liver Enzymes
Liver enzymes are enzymes –
Liver enzymes are found in the blood normally, but only in a certain range of concentration. When liver enzymes are found in the blood over and above the normal range, that can be an indicator of liver diseases. Although the liver produces a huge number of enzymes (with the possible exception of the brain, it’s arguably the most complex organ in the human body), there are several that are especially important for diagnostic purposes. Some of those follow.
Alanine Transaminase (ALT)
Possibly the single most important liver enzyme for purposes of diagnosing liver disease , alanine transaminase or ALT is measured by a very common blood test. When significantly elevated above normal levels, ALT can indicate damage to liver cells. This can arise from many different causes including physical trauma to the liver, hepatitis, fatty liver disease , early indicators of serious liver problems such as liver cancer or cirrhosis , congestive heart failure, diabetes, bile duct blockage, and mono. Obviously not all of these are liver diseases.
Because of the wide range of problems that elevated ALT can indicate, follow-
Aspartate Transaminase (AST)
Another very important enzyme for diagnosis is aspartate transaminase or AST. AST is found in the heart, skeletal muscles, brain, kidneys, and red corpuscles. Elevated AST can be the result of damage to or abnormalities in any of these, so even more than ALT it’s not a clear and unambiguous sign of liver damage when it’s elevated. However, it usually does indicate some sort of medical problem and trouble with the
heart or brain is also cause for concern. AST is considered a major heart disease marker.
Another common test when diagnosing liver disease is to compare the levels of AST to those of ALT . This ratio can be a sign of hepatitis or liver cancer when it’s above 2.0 (i.e., AST elevated to twice the level of ALT). When the ratio is between 1 and 2, that’s a common sign of cirrhosis of the liver, and when it’s below 1 (i.e., ALT elevated above AST), other liver diseases are indicated.
Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP)
Alkaline phophatase is primarily found in the bile ducts and the liver cells that line the bile ducts. For that reason, elevations of alkaline phosphatase can show obstruction of the bile ducts or other problems impeding the flow of bile from the liver to the duodenum, although it also is an indicator of several other liver diseases. However, higher-
and some other people who are showing high rates of tissue growth especially of the bone tissues.
Gamma Glutamyl Transpeptidase (GGT)
This enzyme’s elevation is a more reliable indicator of liver disease than ALT, which is preferentially used as a first-
5′ Nucleotidase
Another follow-
Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH)
This enzyme is a product of tissue breakdown anywhere in the body, so it’s not a specific for liver disease, and a test for elevated LDH has a lot of uses in medicine and diagnosis. It’s particularly good as an indicator of cancer, since cancer cells are more prone to breakdown than healthy cells. So this is a very broad diagnostic indicator and its primary utility in liver disease diagnosis is that, once liver problems have been identified by other tests, elevated LDH is an indicator of liver cancer rather than other liver diseases.
Best foods for liver. The 9 best and worst foods for your liver

If you were to make a list of the most important organs in our body, the usual suspects would probably come to mind. Your heart, brain and kidneys would likely top that list. However, you might forget about one organ that is absolutely vital to living a healthy life — your liver.
Not only is your liver the second largest organ in your body, it performs more than 500 functions that keep your body at its best. From processing and storing nutrients to balancing blood sugar, fueling muscles, regulating blood clotting and filtering toxins from your bloodstream, your liver is always hard at work.
With that in mind, let’s take a deep dive into the foods that love your liver and the foods your liver would love for you to forget.
#1 – Oatmeal
Foods like oatmeal which are rich input your liver on the fast track to better health. Research has demonstratedlurking around your belly, hips and thighs, which is a great way to keep your liver functioning at its best and ward off a fatty liver.
#2 – Broccoli
Eating plenty of fresh veggies is a must to guard your liver against disease. And broccoli is one of the best. That’s because when your body metabolizes cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli,is created. This molecule regulates the actions of a number of key proteins associated with inflammation, immunity, cellular health and even hormone metabolism — making it a liver health powerhouse.
#3 – Coffee
If you can’t start your day without the jolt of caffeine from your favorite morning beverage, no worries! Studies have actually shown that coffee is liver-protective thanks to two ingredients —. These diterpenes reduce oxidative stress and increase the expression of glutathione, your body’s most important antioxidant. Just be sure to go for ground coffee rather than instant, since it offers higher levels of both.

Peak Liver Support™
All toxic chemicals disrupt the endocrine system, which negatively impacts your hormones. But toxins don’t just cause hormones to go haywire. They change your metabolism so your body becomes a storage unit for toxin-filled fat cells that… MORE 〉〉
〈www.PeakNatural.com〉
«SPONSORED»
#4 – Green tea
Green tea is a major source of antioxidants known as catechins. One of these catechins — epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) has been shown in research to. And green tea is well-known for the protection it offers against some types of cancer, including that of the liver, due to its ability to.
#5 – Almonds
Almonds are especially rich in vitamin E, an antioxidant that according to research published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, may. Other nuts that areinclude walnuts, pistachios, cashews and Brazil nuts.
#6 – Asparagus
Alcohol damages your liver by causing cell toxicity and oxidative stress. However, research has shown that the minerals and amino acids inprovide potent hangover prevention while guarding liver cells against toxins.
#7 – Blueberries
Fruits such as blueberries and plums and even rich indulgences such as dark chocolate are packed with compounds known as polyphenols. These compounds not only helpby working to lower your blood pressure, boost your immune system, and fuel your brain, they may also help nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. You can increase their health effects 10 times by pairing them with milk!
Keep these foods far from your liver
French fries
Some of the most important foods to avoid to keep your liver healthy are foods that are high in saturated fats. Whether it’s French fries, potato chips or burgers,, accelerating inflammation which can lead to liver scarring or cirrhosis.
Sugar
Sugar might taste sweet but it’s not a sweet choice for liver health. In fact, your liver has the job of converting the sugar you eat into fat. This means that the more sugar you eat, the more fat your liver makes and the more that can stick around inside the organ causing fatty liver disease. And if you have prediabetes or prediabetes, sugar can double your risk for fatty liver. This also makes it easy to see why high sugar intake is.
Unfortunately, this also holds true for a sugar you might consider healthy since it comes from fruit —.
Bonus tip:
We all know that drinking too much, even if only occasionally, is one of the worst things you can do to your liver. The key is to stick to just one drink per day if you’re a woman or two for men.
And always drink plenty of water, rather than fruit juices or sodas which are packed with sugar, in order to keep your body hydrated and your liver at its best.
Editor’s note: Are you feeling unusually tired? You may think this is normal aging, but the problem could be your master hormone. When it’s not working, your risk of age-related diseases skyrockets. To reset what many call “the trigger for all disease” and live better, longer, click here to discover The Insulin Factor: How to Repair Your Body’s Master Controller and Conquer Chronic Disease!
Liver Health. Liver Awareness Month Feature
The best way to fight liver disease is to avoid it, if at all possible. Here are 13 tried and true ways to have a healthy liver!
- Maintain a healthy weight. If you’re obese or even somewhat overweight, you’re in danger of having a fatty liver that can lead to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), one of the fastest growing forms of liver disease. Weight loss can play an important part in helping to reduce liver fat.
- Eat a balanced diet. Avoid high calorie-meals, saturated fat, refined carbohydrates (such as white bread, white rice and regular pasta) and sugars. Don’t eat raw or undercooked shellfish. For a well-adjusted diet, eat fiber , which you can obtain from fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grain breads, rice and cereals. Also eat meat (but limit the amount of red meat), dairy (low-fat milk and small amounts of cheese) and fats (the “good” fats that are monounsaturated and polyunsaturated such as vegetable oils, nuts, seeds, and fish). Hydration is essential, so drink a lot of water.
- Exercise regularly. When you exercise consistently, it helps to burn triglycerides for fuel and can also reduce liver fat.
- Avoid toxins. Toxins can injure liver cells. Limit direct contact with toxins from cleaning and aerosol products, insecticides, chemicals, and additives. When you do use aerosols, make sure the room is ventilated, and wear a mask. Don’t smoke.
- Use alcohol responsibly. Alcoholic beverages can create many health problems. They can damage or destroy liver cells and scar your liver. Talk to your doctor about what amount of alcohol is right for you. You may be advised to drink alcohol only in moderation or to quit completely.
- Avoid the use of illicit drugs. In 2012, nearly 24 million Americans aged 12 or older were current illicit drug users, meaning they had used an illicit drug during the month prior to the survey interview. This estimate represents 9.2 percent of the population aged 12 or older. Illicit drugs include marijuana/hashish, cocaine (including crack), heroin, hallucinogens, inhalants, or prescription-type psychotherapeutics (pain relievers, tranquilizers, stimulants, and sedatives) used non-medically.
- Avoid contaminated needles. Of course, dirty needles aren’t only associated with intravenous drug use. You ought to follow up with a medical practitioner and seek testing following any type of skin penetration involving sharp instruments or needles. Unsafe injection practices, though rare, may occur in a hospital setting, and would need immediate follow-up. Also, use only clean needles for tattoos and body piercings.
- Get medical care if you’re exposed to blood. If for any reason you come into contact with someone else’s blood, immediately follow up with your doctor. If you’re very concerned, go to your nearest hospital’s emergency room.
- Don’t share personal hygiene items. For example, razors, toothbrushes and nail clippers can carry microscopic levels of blood or other body fluids that may be contaminated.
- Practice safe sex. Unprotected sex or sex with multiple partners increases your risk of hepatitis B and hepatitis C.
- Wash your hands. Use soap and warm water immediately after using the bathroom, when you have changed a diaper, and before preparing or eating food.
- Follow directions on all medications. When medicines are taken incorrectly by taking too much, the wrong type or by mixing medicines, your liver can be harmed. Never mix alcohol with other drugs and medications even if they’re not taken at the same time. Tell your doctor about any over-the-counter medicines, supplements, and natural or herbal remedies that you use.
- Get vaccinated. There are vaccines for hepatitis A and hepatitis B. Unfortunately, there’s no vaccine against the hepatitis C virus.





